Highly improved electrochemical performances of LiCoO2via a multi-element co-doping strategy
Abstract
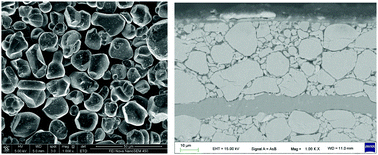
Due to its high compact density and high specific capacity, LiCoO2 has become the most widely used cathode material in the field of consumer electronics and appliances. Increasing the working voltage of the cathode material is an effective strategy for fabricating higher-energy-density Li-ion rechargeable batteries. However, increasing the working voltage usually leads to a series of problems, such as rapid capacity attenuation, especially under high temperature conditions. By using a combinatorial multi-element co-doping strategy, we synthesized a novel Li-ion electrode material named LCO-D. Ti, Mg, and La were doped in Al-doped Co3O4 during the solid-phase sintering process. Multi-element co-doping was shown to be effective in inhibiting the phase transition at 4.2 V, alleviating the irreversibility of phase transition at 4.55 V, and reducing the internal stress in the LCO-D particles. The structural and thermal stability of the LCO-D was greatly improved. The multi-element co-doping was also beneficial to the cycle performance of LCO-D under high voltage and high temperature conditions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...