Computational identification of human ubiquitination sites using convolutional and recurrent neural networks†
Abstract
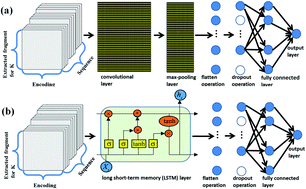
Ubiquitination is a very important protein post-translational modification in humans, which is closely related to many human diseases such as cancers. Although some methods have been elegantly proposed to predict human ubiquitination sites, the accuracy of these methods is generally not very satisfactory. In order to improve the prediction accuracy of human ubiquitination sites, we propose a new ensemble method HUbipPred, which takes the binary encoding and physicochemical properties of amino acids as training features, and integrates two intensively trained convolutional neural networks and two recurrent neural networks to build the model. Finally, HUbiPred achieves AUC values of 0.852 and 0.844 in five-fold cross-validation and independent tests, respectively, which greatly improves the prediction accuracy compared to previous predictors. We also analyze the physicochemical properties of amino acids around ubiquitination sites, study the important roles of architectures (i.e., convolution, long short-term memory (LSTM) and fully connected hidden layers) in the networks for prediction performance, and also predict potential ubiquitination sites in humans using HUbiPred. The training and test datasets, predicted human ubiquitination sites, and source codes of HUbiPred are publicly available at https://github.com/amituofo-xf/HUbiPred.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...