Toward autonomous design and synthesis of novel inorganic materials
Abstract
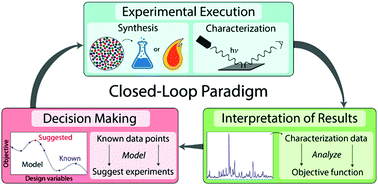
Autonomous experimentation driven by artificial intelligence (AI) provides an exciting opportunity to revolutionize inorganic materials discovery and development. Herein, we review recent progress in the design of self-driving laboratories, including robotics to automate materials synthesis and characterization, in conjunction with AI to interpret experimental outcomes and propose new experimental procedures. We focus on efforts to automate inorganic synthesis through solution-based routes, solid-state reactions, and thin film deposition. In each case, connections are made to relevant work in organic chemistry, where automation is more common. Characterization techniques are primarily discussed in the context of phase identification, as this task is critical to understand what products have formed during synthesis. The application of deep learning to analyze multivariate characterization data and perform phase identification is examined. To achieve “closed-loop” materials synthesis and design, we further provide a detailed overview of optimization algorithms that use active learning to rationally guide experimental iterations. Finally, we highlight several key opportunities and challenges for the future development of self-driving inorganic materials synthesis platforms.
- This article is part of the themed collections: Materials Horizons 10th anniversary regional spotlight collection: The Americas and Recent Review Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
