Modulation of a host’s cell membrane nano-environment by mycobacterial glycolipids: involvement of PI(4,5)P2 signaling lipid?†
Abstract
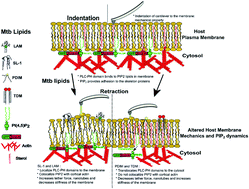
Virulence-associated glycolipids from Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) act as effector molecules during infection—in addition to proteins. Upon insertion, they alter the host cell’s membrane properties modifying the host’s functions to aid Mtb survival and disease course. Here we combine tether force experiments and microscopy to reveal previously unknown insights on the potential involvement of the phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PI(4,5)P2) lipid in the Mtb lipid–host interaction landscape. Our data shows that Mtb lipids, having different structural and chemical make-up, distinctly alter a host’s PI(4,5)P2 membrane abundance/organization and PI(4,5)P2-actin colocalization, thus impacting the plasma membrane–cytoskeletal adhesion forces. Combined with our previous findings that underscore the role of exogenous Mtb lipids in remodeling host plasma membrane organization and mechanics, this work builds upon a lipid-centric view of tubercular infections. Dynamically changing a host’s plasma membrane lipid content – in response to virulent lipids – might represent a so far unexplored mechanism invoked by Mtb to modulate the host cell’s adhesive properties to escape immune surveillance. These findings will deepen our collective understanding of the functional role of Mtb lipids in hijacking the host cell processes amenable to pharmacological inhibition.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Peptide-membrane interactions


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...