Coagulation of organic pollutants by Moringa oleifera protein molecules: in silico approach†
Abstract
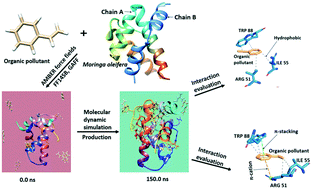
Availability of clean water for various activities is a global challenge. Moringa oleifera (MO) seed protein extract has been identified as a natural coagulant for wastewater treatment. The mechanistic understanding of the coagulating activity of MO is poor. This study employed molecular dynamics simulation to predict and investigate the coagulation ability of known MO seed protein for the removal of four organic pollutants two of which had been previously examined experimentally. The results provide insights relating to the amino acid residues in MO and their types of interaction. An average of 80 to 90% of the pollutant ligands (average of 8 to 9 molecules out of 10 used) was found to coagulate around the MO at the end of 150 ns simulation time. The binding free energy reported was within the range of −149.88 to −51.24 kcal mol−1. Amino acid residues from both chains A and B of MO were observed to participate in the protein–ligand interactions. Many amino acid residues of MO play a significant role in the interaction of the pollutants during the simulation with their binding energies ranging from −3.925 to −1.027 kcal mol−1. Stability was reported for the MO–pollutant complexes which were observed to be strengthened majorly through hydrophobic and hydrogen bonding. The results from this investigation place more clarity on the coagulation ability of MO and give insight into the molecular activity of MO for wastewater treatment.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Environmental Science: Water Research & Technology Recent HOT Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...