Antifouling sandwich-structured electrospun nanofibrous membranes by integrating fluffy and hydrophobic layers for long-term airborne particulate matter segregation†
Abstract
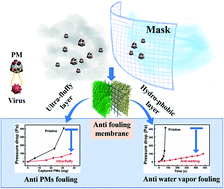
Pollution from airborne particulate matter (PM), which can cause various respiratory diseases and viral and bacterial infections, has become a threat to public health. To ensure personal breathing safety, enormous efforts have been devoted to developing efficient filters to segregate PM. Among them electrospun nanofibrous membranes (ENMs) have received wide attention. However, pore blocking resulting from the formation of PM and/or water fouling layers remains a concern in their long-term utilization. Herein, we report a sandwich structure combining a fluffy layer and a hydrophobic layer to tackle this challenge, namely the polyacrylonitrile–silicon dioxide/polyester/polyvinylidene fluoride (PAN-SiO2/PET/PVDF) ENM. Expressly, to relieve the generation of PM fouling layers, a fluffy PAN-SiO2 nanofiber layer with a large pore size and spacing between adjacent nanofibers was constructed by embedding micro-scale SiO2 particles into the nanofibers. Furthermore, to avoid forming a water fouling layer, a hydrophobic PVDF nanofiber layer was constructed on the side close to the breathing part. This unique structure endows the PAN-SiO2/PET/PVDF ENM with stable permeability and competitive PM segregation efficiency. We anticipate that the developed system will be helpful to produce ENM based mask filters with antifouling properties for personal protection.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Nanomaterials in air


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...