Elucidation of substrate interaction effects in multicomponent systems containing 3-ring homocyclic and heterocyclic polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons†
Abstract
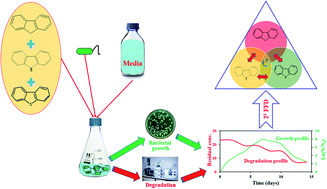
Bacterial growth and degradation experiments were conducted on carbazole (CBZ), fluorene (FLU) and dibenzothiophene (DBT) individually and in various mixture combinations using an efficient polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) degrading bacterial strain, Pseudomonas aeruginosa RS1. In single component systems, bacterial growth on CBZ (specific growth rate, μ = 0.99 day−1) was much higher compared to that on FLU (μ = 0.38 day−1) and DBT (μ = 0.33 day−1) and bacterial growth was inhibited in the presence of FLU and DBT in binary (μ = 0.64 day−1) and ternary (μ = 0.75 day−1) mixtures. Multisubstrate additive modelling indicated growth inhibition in all the systems. The degradation of the compounds was significantly inhibited in binary mixtures. While the degradation of the compounds in binary mixtures varied from 35 ± 4% to 73 ± 3%, their degradation varied from 61 ± 5% to 91 ± 4%, when applied as sole substrates and from 77 ± 3% to 96 ± 3%, when applied in a ternary mixture. Degradation experiments were also conducted in ternary mixtures using a 23 full factorial design and the results were examined using analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Tukey's honest significant difference (HSD) tests. At a low concentration of the heterocyclics, CBZ and DBT (5 mg L−1 each), the degradation of the PAH, FLU, was significantly enhanced (from 81 ± 1% to 93 ± 0.3%) when its concentration was increased from 5 to 30 mg L−1. The full factorial design can provide valuable insights into substrate interaction effects in mixtures.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Contaminant remediation and fate


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...