Defect-free-induced Na+ disordering in electrode materials†
Abstract
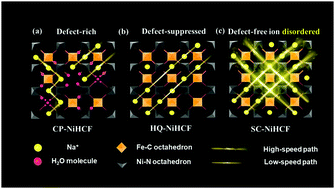
For reaching high-performance of electrode materials, it is generally believed that understanding the structure evolution and heterogeneous alignment effect is the key. Presently, a very simple and universally applicable self-healing method is investigated to prepare defect-free Prussian blue analogs (PBAs) that reach their theoretical capacity as cathode materials for sodium-ion batteries (SIBs). For direct imaging of the local structure and the dynamic process at the atomic scale, we deliver a fast ion-conductive nickel-based PBA that enables rapid Na+ extraction/insertion within 3 minutes and a capacity retention of nearly 100% over 4000 cycles. This guest-ion disordered and quasi-zero-strain nonequilibrium solid–solution reaction mechanism provides an effective guarantee for realizing long-cycle life and high-rate capability electrode materials that operate via reversible two-phase transition reaction. Unconventional materials and mechanisms that enable reversible insertion/extraction of ions in low-cost metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) within minutes have implications for fast-charging devices, grid-scale energy storage applications, material discovery, and tailored modification.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...