α-Substituted phthalocyanines based on metal-induced H- or J-type aggregation for silver and palladium ions: synthesis, fluorescence, and antimicrobial and antioxidant properties†
Abstract
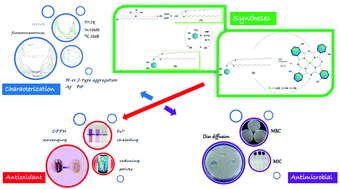
In this study, firstly, 3-(2,3-bis(hexadecylthio)propoxy)phthalonitrile (2) as a new phthalonitrile derivative was prepared. Then, new types of non-peripheral phthalocyanine derivatives [CuPc (3), ZnPc (4), and CoPc (5)] were synthesized by using this ligand. The synthesized new compounds were characterized by common spectroscopic methods such as FTIR, 1H-NMR, 13C-NMR, MALDI-TOF, UV-Vis and fluorescence spectroscopy. The H- or J-type aggregation behaviors of novel type metallophthalocyanines in the presence of valuable metal ions such as Ag(I) and Pd(II) were investigated by UV-Vis and fluorescence spectroscopy. The quenching efficiency of the Ag(I) and Pd(II) ions for ZnPc (4) was obtained using the Stern–Volmer equation and the quenching constant of ZnPc (4) towards Ag(I) and Pd(II) ions was found to be 2.9 × 105 mol L−1 and 1.2 × 105 mol L−1, respectively. The binding constant (Ka) and binding stoichiometry (n) of Ag(I) and Pd(II) ions for ZnPc (5) were calculated using a modified Benesi–Hildebrand equation, and were found to be 1.4 × 108 M−1 and 3.4 × 107 M−1, respectively. The binding ratio and free energy change of Ag(I) and Pd(II) ions for ZnPc (4) were found to be 1.86, 1.54, −46.49 kJ mol−1 and −42.9 kJ mol−1, respectively. Also, the antioxidant properties of the synthesized novel type metallophthalocyanines and their Ag(I) and Pd(II) ion doped aggregates were determined using three different methods: DPPH free radical scavenging activity, ferrous ion chelating activity and reducing power activity. Finally, the antibacterial and antifungal activities of phthalocyanine compounds synthesized within the scope of this study were determined by disc diffusion and macrobroth dilution methods and the effect of the doping of Ag(I) and Pd(II) ions on the antibacterial activities of phthalocyanines was investigated.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...