Heterometallic MOFs constructed from thiophene and furandicarboxylate ligands for heavy metal luminescence sensing†
Abstract
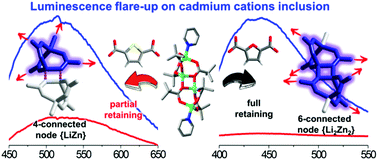
Rational design of a series of new heterometallic MOFs was carried out by the judicious choice of the corresponding synthesis conditions and ligand geometry. Three heterometallic MOFs (H2NMe2)[LiZn(dmf)(tdc)2]·DMF·H2O (1), [{LiZn}2Li2Zn2(dmf)6(tdc)6]·6DMF·H2O (2) and [Li2Zn2(dmf)2(fdc)3]·2DMF·2H2O (3) were obtained on the basis of the pre-synthesized pivalate complex [Li2Zn2(py)2(piv)6]. The angle between carboxylic groups greatly affects the possibility of retaining the initial tetranuclear node in the structure of the obtained MOFs. Compound 3 demonstrates permanent porosity with a calculated BET surface area value of 287 m2 g−1. Compounds 2 and 3 are capable of heavy metal sorption from their nitrate solution, and a significant flare-up of the luminescence of the obtained inclusion compounds is observed, where the quantum yield of luminescence increases by an order of magnitude in the case of cadmium inclusion.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...