An in vitro selective inhibitory effect of silver(i) aminoacidates against bacteria and intestinal cell lines and elucidation of the mechanism of action by means of DNA binding properties, DNA cleavage and cell cycle arrest†
Abstract
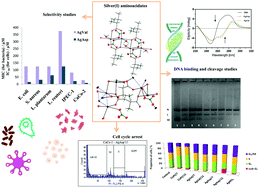
Novel silver(I) aminoacidate complexes {[Ag(HVal)(H2O)(NO3)]}n (AgVal) and {[Ag3(HAsp)2(NO3)]}n·nH2O (AgAsp) were prepared, investigated and fully characterized by vibrational spectroscopy (mid-IR), elemental analysis, thermogravimetric analysis, X-ray crystallography and mass spectrometry. Their stability in D2O and PBS buffer was verified by time-dependent 1H and 13C NMR measurements. Their in vitro antibacterial activity (against pathogenic Staphylococcus aureus CCM4223, Escherichia coli CCM4787) and that against probiotic bacteria Lactobacillus plantarum CCM7102 and Lactobacillus reuteri (L26) were determined and potential dosing concentration was evaluated. The cytotoxicity of both the complexes against intestinal porcine epithelial (IPEC-1) and human epithelial colorectal adenocarcinoma (CaCo-2) cell lines was determined using the colorimetric MTT assay and against human metastatic melanoma (A2058), human pancreatic adenocarcinoma (PaTu 8902), human cervical adenocarcinoma (HeLa), human colorectal carcinoma (HCT116), human leukaemic T cell lymphoma (Jurkat), and human dermal fibroblasts (HDF) using colorimetric MTS assay. The selectivity index (SI) was identified for intestinal cancer (CaCo-2) and healthy (IPEC-1) cells. The mechanism of action of AgVal and AgAsp was further elucidated and discussed by the study of their binding affinity toward the CT DNA, the ability to cleave the supercoiled form of pUC19 DNA and the ability to influence numbers of cells within each cell cycle.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...