Electrocatalytic nitrate reduction on rhodium sulfide compared to Pt and Rh in the presence of chloride†
Abstract
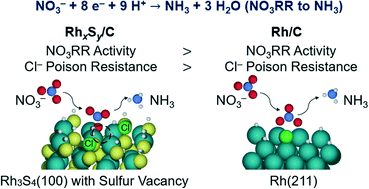
Chloride poisoning is a serious problem for the electrocatalytic reduction of aqueous nitrate (NO3−) and improved electrocatalysts are needed. Here we study the electrocatalytic activity of rhodium sulfide supported on carbon (RhxSy/C) for the reduction of nitrate and compare it against Pt/C and Rh/C in the presence of chloride. Between 0.05–0.15 V vs. RHE, RhxSy/C has a steady-state nitrate reduction current density in 1 M H2SO4 + 1 M NaNO3 that is 1.6–5.6 times greater than Rh/C (the most active metal electrocatalyst) and 10–24 times greater than Pt/C. Current densities are decreased by 37% for RhxSy/C, 62% for Rh/C, and 40% for Pt/C at 0.1 V vs. RHE in the presence of 1 mM chloride. The decrease in nitrate reduction activity for Pt, Rh, and RhxSy is due to the competitive adsorption of chloride and nitrate on the surface. Density functional theory (DFT) modeling predicts that chloride poisoning will persistently inhibit nitrate reduction on metals due to linear adsorbate scaling relations between nitrate and chloride. DFT calculations and microkinetic modeling of our experimental measurements predict that nitrate converts to nitrite via an H-assisted dissociation mechanism on Pt and direct nitrate dissociation on Rh and RhxSy. Pristine RhxSy (i.e., Rh3S4, Rh2S3, and Rh17S15) terraces are predicted to be inactive toward nitrate reduction. In contrast, sulfur vacancies in Rh3S4 terraces are predicted to be active for nitrate reduction, but also bind chloride strongly. Thus, sulfur-defected Rh3S4 rationalize the experimentally observed high activity but moderate chloride poison-resistance of RhxSy/C for nitrate reduction.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Emerging Investigator Series


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
