A comprehensive review on the photocatalytic activity of polythiophene-based nanocomposites against degradation of organic pollutants
Abstract
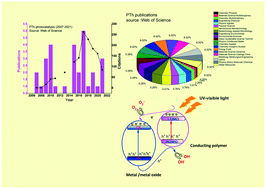
Polythiophene (PTh) and its nanocomposites are considered as promising photocatalytic candidates due to their unique electrical behavior, good environmental stability, low optical band gap, stability in doped/neutral states and in particular the ease of synthesis. Apart from electrical and electronic applications, PTh has shown remarkable performance in photocatalysis. The fabrication of metal oxides with PTh extends the absorption range of PTh-based composite materials, which enhances the photocatalytic activity under UV/UV-visible light irradiation as well as under microwave exposure. PTh-based composites with metals/metal oxides exhibit synergistic photocatalytic properties. The present review therefore highlights the studies dealing with the photocatalytic performance of PTh and its nanocomposites along with their preparation, properties and mechanism of degradation of various kinds of pollutants under UV, visible light, sunlight and microwave irradiation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...