Rational engineering of Acinetobacter tandoii glutamate dehydrogenase for asymmetric synthesis of l-homoalanine through biocatalytic cascades†
Abstract
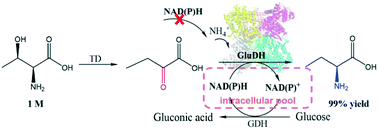
L-Homoalanine, a useful building block for the synthesis of several chiral drugs, is generally synthesized through biocascades using natural amino acids as cheap starting reactants. However, the addition of expensive external cofactors and the low efficiency of leucine dehydrogenases towards the intermediate 2-ketobutyric acid are two major challenges in industrial applications. Herein, a dual cofactor-dependent glutamate dehydrogenase from Acinetobacter tandoii (AtGluDH) was identified to help make full use of the intracellular pool of cofactors when using whole-cell catalysis. Through reconstruction of the hydrophobic network between the enzyme and the terminal methyl group of the substrate 2-ketobutyric acid, the strict substrate specificity of AtGluDH towards α-ketoglutarate was successfully changed, and the activity obtained by the most effective mutant (K76L/T180C) was 17.2 times higher than that of the wild-type protein. A three-enzyme co-expression system was successfully constructed in order to help release the mass transfer restriction. Using 1 M L-threonine, which is close to the solubility limit, we obtained a 99.9% yield of L-homoalanine in only 3.5 h without adding external coenzymes to the cascade, giving 99.9% ee and a 29.2 g L−1 h−1 space–time yield. Additionally, the activities of the engineered AtGluDH towards some other hydrophobic amino acids were also improved to 1.1–11.2 fold. Therefore, the engineering design of some dual cofactor-dependent GluDHs could not only eliminate the low catalytic activity of unnatural substrates but also enhance the cofactor utilization efficiency of these enzymes in industrial applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...