Sulfoglycolysis: catabolic pathways for metabolism of sulfoquinovose
Abstract
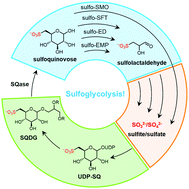
Sulfoquinovose (SQ), a derivative of glucose with a C6-sulfonate, is produced by photosynthetic organisms and is the headgroup of the sulfolipid sulfoquinovosyl diacylglycerol. The degradation of SQ allows recycling of its elemental constituents and is important in the global sulfur and carbon biogeochemical cycles. Degradation of SQ by bacteria is achieved through a range of pathways that fall into two main groups. One group involves scission of the 6-carbon skeleton of SQ into two fragments with metabolic utilization of carbons 1–3 and excretion of carbons 4–6 as dihydroxypropanesulfonate or sulfolactate that is biomineralized to sulfite/sulfate by other members of the microbial community. The other involves the complete metabolism of SQ by desulfonylation involving cleavage of the C–S bond to release sulfite and glucose, the latter of which can enter glycolysis. The discovery of sulfoglycolytic pathways has revealed a wide range of novel enzymes and SQ binding proteins. Biochemical and structural characterization of the proteins and enzymes in these pathways have illuminated how the sulfonate group is recognized by Nature's catalysts, supporting bioinformatic annotation of sulfoglycolytic enzymes, and has identified functional and structural relationships with the pathways of glycolysis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...