The interplay of carbophilic activation and Au(i)/Au(iii) catalysis: an emerging technique for 1,2-difunctionalization of C–C multiple bonds
Abstract
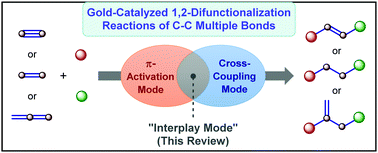
Gold complexes have emerged as the catalysts of choice for various functionalization reactions of C–C multiple bonds due to their inherent carbophilic nature. In a parallel space, efforts to realize less accessible cross-coupling reactivity have led to the development of various strategies that facilitate the arduous Au(I)/Au(III) redox cycle. The interplay of the two important reactivity modes encountered in gold catalysis, namely carbophilic activation and Au(I)/Au(III) catalysis, has allowed the development of a novel mechanistic paradigm that sponsors 1,2-difunctionalization reactions of various C–C multiple bonds. Interestingly, the reactivity as well as selectivity obtained through this interplay could be complementary to that obtained by the use of various other transition metals that mainly involved the classical oxidative addition/migratory insertion pathways. The present review shall comprehensively cover all the 1,2-difunctionalization reactions of C–C multiple bonds that have been realized by the interplay of the two important reactivity modes and categorized on the basis of the method that has been employed to foster the Au(I)/Au(III) redox cycle.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...