Silver oxide model surface improves computational simulation of surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy on silver nanoparticles†
Abstract
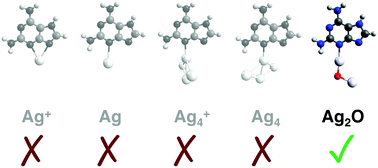
Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) coupled with density functional theory (DFT) computations can characterise the adsorption orientation of a molecule on a nanoparticle surface. When using DFT to simulate SERS on a silver surface, one typically employs an atom (Ag), ion (Ag+), or cluster (Agx or Agx+) as the model surface. Here, by examining the nucleobase 2,6-diaminopurine (2,6-DAP) and then generalising our strategy to three other molecules, we show that employing silver oxide (Ag2O) as the model surface can quantitatively improve the accuracy of simulated SERS.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...