Dynamic behavior of liquid droplets with enzyme compartmentalization triggered by sequential glycolytic enzyme reactions†
Abstract
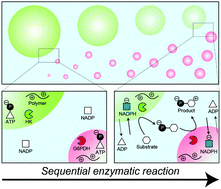
Dynamic droplet formation via liquid–liquid phase separation (LLPS) is believed to be involved in the regulation of various biological processes. Here, a model LLPS system coupled with a sequential glycolytic enzymatic reaction was developed to reproduce the dynamic control of liquid droplets; (i) the droplets, which consist of poly-L-lysine and nucleotides, compartmentalize two different enzymes (hexokinase and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase) individually, accelerating the overall reaction, and (ii) each enzymatic reaction triggers the formation, dissolution and long-term retention of the droplets by converting the scaffold nucleotides. This model system will offer a new aspect of enzymes associated with LLPS in living cells.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...