Pd-Catalyzed and ligand-enabled alkene difunctionalization via unactivated C–H bond functionalization
Abstract
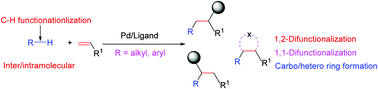
Palladium-catalyzed and ligand-enabled C–H functionalization methods have emerged as a powerful approach for the preparation of therapeutically important motifs and complex natural products. Olefins, owing to their natural abundance, have been extensively employed for the formation of C–C and C–X bonds and the generation of various heterocycles. Traditionally, activated as well as starting materials with preinstalled functional groups, and also halide substrates under transition metal catalysis, have been employed for olefin difunctionalization. However, strategies for employing unactivated C–H bond functionalization to achieve alkene difunctionalization have rarely been explored. A possible solution to this challenge is the application of bulky ligands which enhances the reductive elimination pathway and inhibits β-hydride elimination to selectively yield difunctionalized alkene products. This feature article summarizes the utilization of unreactive C–H bonds in the Pd-catalyzed and ligand-enabled difunctionalization of alkenes.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Functionalization of unreactive C-H bonds


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...