Crystalline assembly of metal–organic polyhedra driven by ionic interactions with polyoxometalates†
Abstract
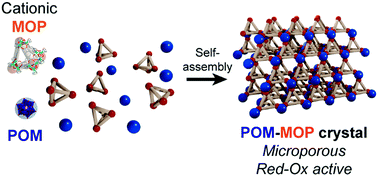
Charge-driven self-assembly of cationic zirconium-based metal–organic polyhedra (MOPs) with polyoxometalates (POMs) leads to a series of porous crystalline salts, prepared by simple mixing of soluble precursors. The reactivity of immobilized POMs was greatly increased, as demonstrated by their fast reduction by hydrazine vapors, without loss of structural integrity.
- This article is part of the themed collection: ChemComm Milestones – First Independent Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...