Encapsulation of bryostatin-1 by targeted exosomes enhances remyelination and neuroprotection effects in the cuprizone-induced demyelinating animal model of multiple sclerosis†
Abstract
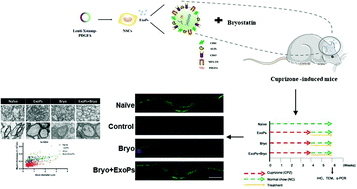
Demyelination is a critical neurological disease, and there is still a lack of effective treatment methods. In the past two decades, stem cells have emerged as a novel therapeutic effector for neural regeneration. However, owing to the existence of the blood–brain barrier (BBB) and the complex microenvironment, targeted therapy still faces multiple challenges. Targeted exosome carriers for drug delivery may be considered a promising therapeutic method. Exosomes were isolated from mice neural stem cells. To develop targeting exosomes, we generated a lentivirus armed PDGFRα ligand that could anchor the membrane. Exosome targeting tests were carried out in vitro and in vivo. The modified exosomes showed an apparent ability to target OPCs in the lesion area. Next, the exosomes were loaded with Bryostatin-1 (Bryo), and the cuprizone-fed mice were administered with the targeting exosomes. The data show that Bryo exhibits a powerful therapeutic effect compared with Bryo alone after exosome encapsulation. Specifically, this novel exosome-based targeting delivery of Bryo significantly improves the protection ability of the myelin sheath and promotes remyelination. Moreover, it blocks astrogliosis and axon damage, and also has an inhibitory effect on pro-inflammatory microglia. The results of this investigation provide a straightforward strategy to produce targeting exosomes and indicate a potential therapeutic approach for demyelinating disease.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...