Molecular engineering of antimicrobial peptide (AMP)–polymer conjugates
Abstract
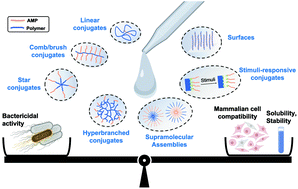
As antimicrobial resistance becomes an increasing threat, bringing significant economic and health burdens, innovative antimicrobial treatments are urgently needed. While antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) are promising therapeutics, exhibiting high activity against resistant bacterial strains, limited stability and toxicity to mammalian cells has hindered clinical development. Attaching AMPs to polymers provides opportunities to present AMPs in a way that maximizes bacterial killing while enhancing compatibility with mammalian cells, stability, and solubility. Conjugation of an AMP to a linear hydrophilic polymer yields the desired improvements in stability, mammalian cell compatibility, and solubility, yet often markedly reduces bactericidal effects. Non-linear polymer architectures and supramolecular assemblies that accommodate multiple AMPs per polymer chain afford AMP–polymer conjugates that strike a superior balance of antimicrobial activity, mammalian cell compatibility, stability, and solubility. Therefore, we review the design criteria, building blocks, and synthetic strategies for engineering AMP–polymer conjugates, emphasizing the connection between molecular architecture and antimicrobial performance to inspire and enable further innovation to advance this emerging class of biomaterials.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Biomaterials Science Emerging Investigators 2021


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...