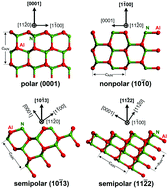
The impacts of pulsed-flow growth on aluminium incorporation in polar (0001), semipolar (10![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) 3) and (11
3) and (11![[2 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0032_0304.gif) 2), as well as nonpolar (10
2), as well as nonpolar (10![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) 0) AlGaN layers have been investigated. The layers were grown simultaneously on differently oriented AlN/sapphire templates by metal–organic vapour phase epitaxy. The AlN mole fraction (0 < xAlN ≤ 0.85) of the layers was varied by simply changing the supply time of the aluminium precursor while keeping nitrogen and gallium precursors constant. Phase separation has been observed for the (0001) and (11
0) AlGaN layers have been investigated. The layers were grown simultaneously on differently oriented AlN/sapphire templates by metal–organic vapour phase epitaxy. The AlN mole fraction (0 < xAlN ≤ 0.85) of the layers was varied by simply changing the supply time of the aluminium precursor while keeping nitrogen and gallium precursors constant. Phase separation has been observed for the (0001) and (11![[2 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0032_0304.gif) 2) layers by X-ray diffraction, and is attributed to their different surface reconstructions during growth. In contrast, no phase separation has been observed for the (10
2) layers by X-ray diffraction, and is attributed to their different surface reconstructions during growth. In contrast, no phase separation has been observed for the (10![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) 0) and (10
0) and (10![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) 3) layers, attributed to their stable surfaces during growth. The AlN mole fraction of the differently oriented layers generally follows the order: (11
3) layers, attributed to their stable surfaces during growth. The AlN mole fraction of the differently oriented layers generally follows the order: (11![[2 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0032_0304.gif) 2) < (0001) < (10
2) < (0001) < (10![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) 3) ≤ (10
3) ≤ (10![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) 0), attributed to their different surface dangling-bond densities. By means of room-temperature photoluminescence measurements, high carbon-incorporation has quantitatively been found in all the layers.
0), attributed to their different surface dangling-bond densities. By means of room-temperature photoluminescence measurements, high carbon-incorporation has quantitatively been found in all the layers.