Role of excess tellurium on the electrical and thermal properties in Te-doped paracostibite†
Abstract
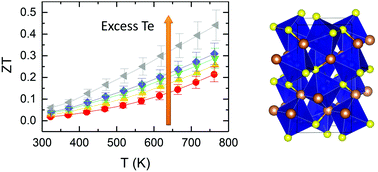
The effect of excess Te in the preparation of synthetic mineral paracostibite, CoSbS, was investigated in an attempt to produce a nano–micro-porous architecture. While the latter was found to have no significant impact, we demonstrate that such strategy is a successful approach to enhance both electrical and thermal property via the formation of a more Te-rich paracostibite phase compared with conventional substitution. Tuning of the electrical properties led to a large power factor of 2150 μW m−1 K−2 at 765 K while the lattice thermal conductivity was reduced by ca. 45%, mainly due to an increased electron–phonon scattering. Ultimately, a maximum ZT of 0.45 was achieved, representing a 100% improvement over conventional Te-doped paracostibite.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...