Consecutive dephosphorylation by alkaline phosphatase-directed in situ formation of porous hydrogels of SF with nanocrystalline calcium phosphate ceramics for bone regeneration†
Abstract
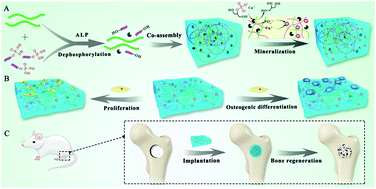
Alkaline phosphatase, as an enzyme involved in the process of bone mineralization and regeneration, was incorporated into a solution of SF to induce its gelation and mineralization through consecutive dephosphorylation actions on different substrates. In these processes, alkaline phosphatase firstly worked on a small peptide of NapGFFYp by removing its hydrophilic phosphate group. The resulted NapGFFY performed supramolecular assembly in the solution of SF and synergistically induced the conformation transition of SF from random coil to β-sheet structures, leading to the formation of a stable SF hydrogel under physiological conditions. And then, the entrapped ALP within the SF–NY gel network retained its catalytic activity, released phosphate ions from glycerophosphate, and catalysed the formation of calcium phosphate minerals within the porous gel. Because of the mild conditions of these processes and good biocompatibility of the scaffold, the mineralized SF gel can work as a biomimetic scaffold to promote the osteogenic differentiation of rBMSCs and stimulate femoral defect regeneration in a rat model.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Journal of Materials Chemistry B HOT Papers


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...