Origins of the peroxidase mimicking activities of graphene oxide from first principles†
Abstract
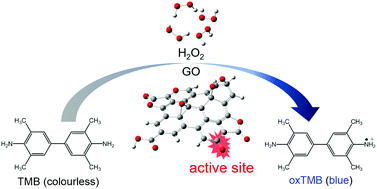
Graphene-based nanomaterials, including graphene oxide (GO) and reduced graphene oxide (rGO), play key roles in the nanozyme field. GO and rGO carrying various oxygen-containing functional groups, including epoxy, hydroxyl, ether, endoperoxide, carbonyl, carboxyl, and ester, have been reported to display peroxidase mimicking activities. However, the active center and the underlying mechanism responsible for its peroxidase mimicking activities still remain unclear. Herein, taking the oxidation of 3,3,5,5-tetramethylbenzidine (TMB) by H2O2 as the model reaction, we investigate the possible catalytic mechanisms using DFT calculations. The results indicate that the carbonyl groups are the active centers. The activation of the C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O bond is the key step in the catalytic cycle. The results will help realize the rational design of carbon-based nanozymes.
O bond is the key step in the catalytic cycle. The results will help realize the rational design of carbon-based nanozymes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...