A novel injectable starch-based tissue adhesive for hemostasis
Abstract
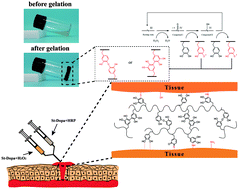
Hemorrhage remains one of the direct causes of high mortality. The development of ideal hemostatic materials with sound ability to deal with severe wound is urgent needed. Although starch-based hemostatic powder has been widely used, hydrous physiological environments severely hamper its binding to the target tissue, thereby limiting the effectiveness in hemostasis. Herein, inspired by mussel adhesive protein, a novel injectable tissue-adhesive hydrogel (St-Dopa hydrogel) composed of starch, succinic anhydride and dopamine was developed in situ by enzymatic crosslinking. The results show that St-Dopa hydrogels were intimately integrated with biological tissue and formed robust barriers to reduce blood loss. St-Dopa hydrogels exhibited superior capacity for in vitro and in vivo hemostasis as compared with chitin hydrogels. In addition to the ease of operation, St-Dopa hydrogels exhibited rapid sol–gel transition, porous microscopic morphology, good swelling ratio and biodegradability, tissue-like elastomeric mechanical properties and excellent cyto/hemo-compatibility. These results suggest that this newly developed St-Dopa hydrogel is a promising biological adhesive and hemostatic material.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Journal of Materials Chemistry B Lunar New Year collection 2021


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...