The design and characterization of a hypersensitive glucose sensor: two enzymes co-fixed on a copper phosphate skeleton†
Abstract
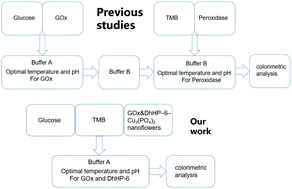
In this study, we first reported a new glucose sensor for the preparation of a glucose oxidase (GOx)-conjugated novel artificial peroxidase mimic deuterohemin peptide (Dh-Ala-His-Thr-Val-Glu-Lys, DhHP-6) (GOx&DhHP-6–Cu3(PO4)2) in order to determine the glucose concentration. The same catalytic environment (pH 7.0, 35 °C) between glucose oxidase (GOx) and DhHP-6 ensured their utilization in catalytic cascade reactions. DhHP-6 and GOx were co-fixed on a copper phosphate skeleton, which ensured resistance toward harsh environments and improved storage stability. Meanwhile, the sensor reduced the diffusion of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) in solutions by immobilization. GOx&DhHP-6–Cu3(PO4)2 possessed a wide linear range of 5–2000 μM, and a limit of detection of 0.5 μM. Based on the above-mentioned results, a new method to rapidly detect glucose concentrations was successfully developed using GOx&DhHP-6–Cu3(PO4)2 nanoflowers with high sensitivity and an easily applied methodology.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...