The impact of carbonate salts on char formation and gas evolution during the slow pyrolysis of biomass, cellulose, and lignin†
Abstract
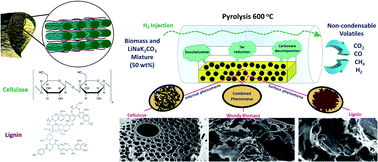
This study deals with the modification of chars derived from different biomass samples (woody biomass, cellulose and lignin). Chars are formed during slow pyrolysis on addition of alkali ternary eutectic salts (Li2CO3: 43.5%, Na2CO3: 31.5%, K2CO3: 25% mol), subjected to two different higher heating temperatures (350 °C and 600 °C). It is shown here that the addition of a carbonate eutectic affects char-making reactions through: tar generation modification, changes in the emitted volatile molecules, alteration of surface oxygenate bonds as well as transformation in the morphology of the remnant char. Initial results using Differential Thermal Gravimetric Analysis (DTG) show that, in carbonate treated samples, char yield is increased at both temperatures investigated. In treated cellulose, a reduced temperature onset of mass loss is observed, expected to be from modified depolymerisation and inhibition of levoglucosan formation for samples heated to both 350 °C and 600 °C. Gas analysis by micro-GC proves that carbonate is involved in the cracking of condensable volatiles, which generates a highly porous char structure and increases the emission of non-condensable volatiles. In addition, SEM results for carbonate treated cellulose demonstrate extensive pore generation including both surface and internally generated pores and interconnected tunnel-like structures at higher temperature (600 °C). This was not reflected however in BET results due to the melted salt blocking the available internal porous structure. Improvement in BET results for chars produced at 600 °C was regardless seen on carbonate addition in both biomass (improving from 371 m2 g−1 to 516 m2 g−1) and lignin (improving from 11 m2 g−1 to 209 m2 g−1).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...