Sn dendrites for electrocatalytic N2 reduction to NH3 under ambient conditions†
Abstract
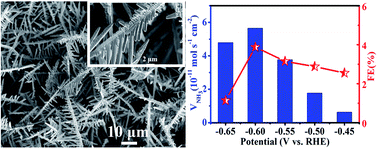
Industrial-scale synthesis of NH3 mainly relies on the energy-intensive Haber–Bosch technology, which not only needs harsh conditions but also produces a large amount of CO2. Electrochemical N2 reduction is regarded as an environmentally friendly method for artificial N2-to-NH3 conversion, but needs efficient catalysts for the N2 reduction reaction (NRR). Here, we report that Sn dendrites on Sn foil act as a non-noble-metal electrocatalyst for the electrochemical NRR under ambient conditions. This electrocatalyst affords an NH3 yield of 5.66 × 10−11 mol s−1 cm−2 and a Faraday efficiency of 3.67% at −0.60 V versus the reversible hydrogen electrode in 0.1 M PBS (pH = 7.0), with high electrochemical durability.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...