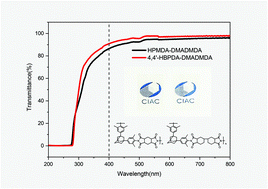
In this study, three adamantane-containing diamines, i.e. 1,3-bis(4-aminophenyl) adamantane (ADMDA), 1,3-bis(3,5-dimethyl-4-aminophenyl) adamantane (DMADMDA) and 1,3-bis(fluoro-aminophenyl) adamantane (FADMDA), were successfully synthesized by Friedel–Crafts alkylation reactions between 1-adamantanol and acetanilide or its analogues, followed by hydrolysis with aqueous NaOH solution. Three regio-isomers were formed in the case of FADMDA due to the occurrence of both para- and ortho-alkylation (relative to the amino groups). Three series of semi-alicyclic polyimides were subsequently produced through a conventional one-step solution polycondensation between the as-developed diamines and commercial dianhydrides. The properties of the synthesized polyimides were characterized with respect to their thermal, mechanical and optical properties. The adamantane-containing polyimides exhibited significantly high glass transition temperatures (Tg) in the range 285–440 °C, excellent optical transparency (>80% transmittance at 400 nm) and optimal thermal and mechanical properties. The substituents in diamines significantly impacted the properties of the resulting polyimides. Specifically, the polyimides from DMADMDA demonstrated higher d-spacing, higher Tg, lower coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE), better optical properties and inferior tensile properties relative to the ADMDA-derived polymers, which could be attributed to the enhanced chain rigidity and reduced inter- and intra-molecular interactions associated with the two bulky methyl groups. In contrast, the FADMDA-derived polymers exhibited lower d-spacing, lower Tg, higher CTE, higher tensile modulus and lower elongation at break than the ADMDA-based ones, due to the reduced chain linearity regularity caused by the ortho-alkylated isomers, as well as suppressed intramolecular interaction originating from the strongly electron-withdrawing fluorine atoms. The excellent comprehensive properties of the adamantane-containing polyimides render these materials promising candidates for a variety of optical and optoelectronic applications.