Silylium cation initiated sergeants-and-soldiers type chiral amplification of helical aryl isocyanide copolymers†
Abstract
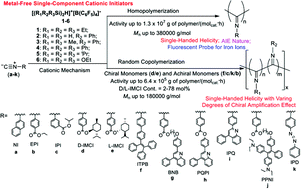
A series of silylium cations [(R1R2R3Si)2H]+[B(C6F5)4]− (1–6) (1: R1 = R2 = R3 = Et; 2: R1 = R3 = H, R2 = Ph; 3: R1 = R3 = Me, R2 = Ph; 4: R1 = R2 = R3 = Ph; 5: R1 = R2 = R3 = iPr; 6: R1 = R2 = R3 = OEt) serve as highly efficient metal-free single-component cationic initiators for the cationic polymerization and copolymerization of chiral and achiral aryl isocyanides R–N![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) C (a–k) (a: R = 2-C10H7 (NI); b: R = 4-(COOEt)–C6H4 (EPI); c: R = 3-[COOiPr]–C6H4 (IPI); d: R = 4-{COO-[(1S,2R,5S)-(2-iPr–5-Me–C6H6)]}–C6H4 (D-IMCI); e: R = 4-{COO-[(1R,2S,5R)-(2-iPr–5-Me–C6H6)]}–C6H4 (L-IMCI); f: R = 4-[4-(Ph)C
C (a–k) (a: R = 2-C10H7 (NI); b: R = 4-(COOEt)–C6H4 (EPI); c: R = 3-[COOiPr]–C6H4 (IPI); d: R = 4-{COO-[(1S,2R,5S)-(2-iPr–5-Me–C6H6)]}–C6H4 (D-IMCI); e: R = 4-{COO-[(1R,2S,5R)-(2-iPr–5-Me–C6H6)]}–C6H4 (L-IMCI); f: R = 4-[4-(Ph)C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C(Ph)2–C6H4]–C6H4 (ITPB); g: R = 4-{COO–(CH2)9–O–[4-(4-Ph–2-C9H5N)–C6H4]}–C6H4 (BNB); h: R = 4-{COO-[4-(4-Ph–2-C9H5N)–C6H4]}–C6H4 (PQPI); i: R = 4-(4-Ph–2-C9H5N)–C6H4 (IPQ); j: R = 4-{COO–(CH2)9–O–[4-(Ph)C
C(Ph)2–C6H4]–C6H4 (ITPB); g: R = 4-{COO–(CH2)9–O–[4-(4-Ph–2-C9H5N)–C6H4]}–C6H4 (BNB); h: R = 4-{COO-[4-(4-Ph–2-C9H5N)–C6H4]}–C6H4 (PQPI); i: R = 4-(4-Ph–2-C9H5N)–C6H4 (IPQ); j: R = 4-{COO–(CH2)9–O–[4-(Ph)C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C(4-N(C2H5)2–C6H4)2–C6H4]}–C6H4 (PPNI); k: R = 4-(N
C(4-N(C2H5)2–C6H4)2–C6H4]}–C6H4 (PPNI); k: R = 4-(N![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N–Ph)–C6H4 (IPD)). Nine homopoly(aryl isocyanide)s are prepared, in which optically active poly(d) and poly(e) exhibit obvious negative and positive Cotton effects at 364 nm and adopt one-handed helical conformations, the poly(f) containing tetraphenylethylene (TPE) substituent shows an aggregation-induced emission (AIE) nature, and the poly(g) containing 2,4-diphenylquinoline (DPQ) substituent serves as a new fluorescent probe for the detection of Fe3+ or Fe2+ ions. By fine-tuning the types of chiral and achiral aryl isocyanides, different degrees of chiral amplification of copolymer helicity can be achieved in the copolymerization of chiral aryl isocyanides d and e with achiral aryl isocyanides b, c, f, and k. Such chiral amplifications of the helical poly(e-co-b)s, poly(d/e-co-c)s, poly(d/e-co-f)s, and poly(d/e-co-k)s with the same helical sense as the corresponding poly(d) and poly(e) obey the “sergeants-and-soldiers” rule. Determination of reactivity ratios of these copolymerizations demonstrates that the different nonlinear relationship between the intensity of CD signals at 364 nm and the D/L-IMCI contents of these copolymers depends on the sequence distribution of chiral aryl isocyanide monomers in these copolymers. Based on the in situ1H NMR, FT-IR, and high resolution ESI-MS spectra, a possible cationic (co)polymerization mechanism is proposed.
N–Ph)–C6H4 (IPD)). Nine homopoly(aryl isocyanide)s are prepared, in which optically active poly(d) and poly(e) exhibit obvious negative and positive Cotton effects at 364 nm and adopt one-handed helical conformations, the poly(f) containing tetraphenylethylene (TPE) substituent shows an aggregation-induced emission (AIE) nature, and the poly(g) containing 2,4-diphenylquinoline (DPQ) substituent serves as a new fluorescent probe for the detection of Fe3+ or Fe2+ ions. By fine-tuning the types of chiral and achiral aryl isocyanides, different degrees of chiral amplification of copolymer helicity can be achieved in the copolymerization of chiral aryl isocyanides d and e with achiral aryl isocyanides b, c, f, and k. Such chiral amplifications of the helical poly(e-co-b)s, poly(d/e-co-c)s, poly(d/e-co-f)s, and poly(d/e-co-k)s with the same helical sense as the corresponding poly(d) and poly(e) obey the “sergeants-and-soldiers” rule. Determination of reactivity ratios of these copolymerizations demonstrates that the different nonlinear relationship between the intensity of CD signals at 364 nm and the D/L-IMCI contents of these copolymers depends on the sequence distribution of chiral aryl isocyanide monomers in these copolymers. Based on the in situ1H NMR, FT-IR, and high resolution ESI-MS spectra, a possible cationic (co)polymerization mechanism is proposed.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...