Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleCreative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence
Correction: Optimization of hydrophobic nanoparticles to better target lipid rafts with molecular dynamics simulations
Xiaoqian
Lin
ab,
Xubo
Lin
 *ab and
Ning
Gu
*ab and
Ning
Gu
 *c
*c
aInstitute of Nanotechnology for Single Cell Analysis (INSCA), Beijing Advanced Innovation Center for Biomedical Engineering, Beihang University, Beijing 100191, China. E-mail: linxbseu@buaa.edu.cn
bSchool of Biological Science and Medical Engineering, Beihang University, Beijing 100191, China
cState Key Laboratory of Bioelectronics, Jiangsu Key Laboratory for Biomaterials and Devices, School of Biological Sciences & Medical Engineering, Southeast University, Nanjing 210096, China. E-mail: guning@seu.edu.cn
First published on 28th July 2020
Abstract
Correction for ‘Optimization of hydrophobic nanoparticles to better target lipid rafts with molecular dynamics simulations’ by Xiaoqian Lin et al., Nanoscale, 2020, 12, 4101–4109, DOI: 10.1039/C9NR09226A.
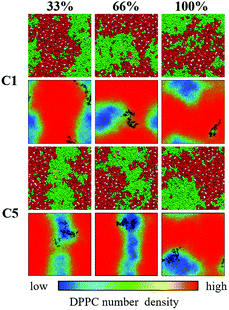
The authors regret that in the original manuscript, Fig. 3 contained a duplicate of the same image in two of the sub-figures. This error does not affect any of the experimental results and discussion or conclusions reported in the paper, only the display of the figure. The correct version of Fig. 3 is shown below, along with the original, unchanged caption. In addition, the ORCID iD previously listed for Professor Ning Gu was incorrect. The correct ORCID iD is: 0000-0003-0047-337X.
The Royal Society of Chemistry apologises for these errors and any consequent inconvenience to authors and readers.
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2020 |