A multifunctional SN38-conjugated nanosystem for defeating myelosuppression and diarrhea induced by irinotecan in esophageal cancer†
Abstract
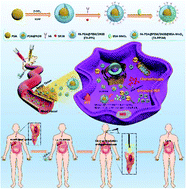
A combination of chemotherapy and phototherapy has been proposed as a promising treatment for esophageal cancer (EC). Irinotecan as a first-line treatment option is widely prescribed for metastatic EC, however, its clinical application is extremely restricted by the low conversion rate to SN38, severe myelosuppression and diarrhea. As a more potent active metabolite of irinotecan, SN38 is a better substitution for irinotecan, but the poor water solubility and the difficulty of encapsulation hindered its medical application. Herein, a multifunctional SN38-conjugated nanosystem (FA-PDA@PZM/SN38@BSA-MnO2, denoted as FA-PPSM) is designed for overcoming the above-mentioned drawbacks and achieving collaborative chemotherapy, photodynamic therapy (PDT) and photothermal therapy (PTT). The tumor acidic microenvironment induces decomposition of BSA-MnO2 nanoparticles into O2 and Mn2+, thus enhancing oxygen-dependent PDT efficacy; meanwhile, Mn2+ can be employed as a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast agent. Under 650 and 808 nm laser irradiation, the FA-PPSM nanocomposites exhibit superior antitumor efficacy in Eca-109-tumor bearing mice. Notably, there is low gastrointestinal toxicity and myelosuppression in the FA-PPSM treated mice compared with those treated with irinotecan (alone). Taken together, this work highlights the great potential of the FA-PPSM nanocomposites for MRI-guided chemotherapy in combination with endoscopic light therapy for esophageal cancer.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...