Nanoscale assembling of graphene oxide with electrophoretic deposition leads to superior percolation network in Li-ion electrodes: TiNb2O7/rGO composite anodes†
Abstract
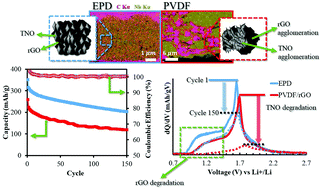
In this paper, electrophoretic deposition (EPD) is shown to promote nanoscale assembling of graphene oxide (GO) enabling the fabrication of highly homogeneous, robust, and capacity fade resistant composite titanium niobate (TiNb2O7, TNO)/rGO anodes upon reductive annealing. Control tests revealed that EPD is superior to conventional PVDF-based casting in maximizing the performance benefits from using reduced GO in Li-ion electrode fabrication as is the case of TNO that is plagued with conductivity and capacity fading problems. In this particular study, we show that there is a synergy developed between GO and EPD with the former (1) stabilizing the EPD suspension, (2) acting as a flexible binder net that affords mechanical integrity during the volume expansion of TNO, (3) serving as a conductive filler, and (4) contributing to Li-ion storage via pseudocapacitance. As a consequence, a superior percolation network is developed. Thus while both EPD- and PVDF- built TNO/rGO composite anodes exhibited high initial capacities (∼350 and 318 mA h g−1) at 0.5 C cycling, respectively, their cycling behaviour was quite different with the latter experiencing high internal polarization and extended degradation. Post-mortem PEEM-XANES analysis clearly demonstrated a highly homogeneous mesostructure in the case of the EPD-built TNO/rGO anode vs. a highly segregated and dis-jointed rGO and TNO component clustering in the PVDF-built electrode.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...