Nanonet-nano fiber electrospun mesh of PCL–chitosan for controlled and extended release of diclofenac sodium†
Abstract
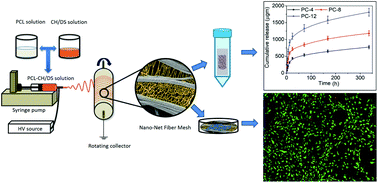
Electrospun nanofiber (EN) technology has been used in the past to generate electrostatically charged multilayer-nanofibers. This platform offers versatile applications including in tissue engineering, drug delivery, wound dressings, and high-efficiency particulate air filters. In this study, we synthesized for the first time nanonet-nanofiber electrospun meshes (NNEMs) of polycaprolactone (PCL)–chitosan (CH) using EN technology. The fabricated NNEMs were utilized for high payload delivery and controlled release of a water-soluble drug. Diclofenac Sodium (DS), a hydrophilic anti-inflammatory drug, was selected as a model drug because of its high aqueous solubility and poor compatibility with insoluble polymers. Various compositions of DS drug-loaded NNEMs (DS-NNEMs) were synthesized. The physicochemical properties such as structure, morphology, and aqueous stability and the chemical properties of DS-NNEMs were evaluated. High drug entrapment efficiency and concentration-dependent drug release patterns were investigated for up to 14 days. Furthermore, the biocompatibility of the DS-NNEMs was tested with NIH 3T3 cells. The physicochemical characterization results showed that the DS drug is a key contributing factor in the generation of nanonet-nanofiber networks during electrospinning. DS-NNEMs also enhanced 3T3 cell adhesion, viability, and proliferation in the nanonet-nano fiber network through the controlled release of DS. The presented EN technology-based biodegradable NNEM material is not only limited for the controlled release of hydrophilic anti-inflammatory drugs, but also can be a suitable platform for loading and release of antiviral drugs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...