Highly aligned carbon nanotubes and their sensor applications†
Abstract
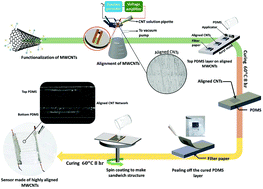
Flexible electronics comprising carbon nanotube (CNT) membranes and polymer composites are used in diverse applications, including health monitoring. Devices prepared using such electronics need to exhibit acceptable sensitivity at high strains, with the advantage of negligible hysteresis. Herein, we report a simple, physically robust method to fabricate a highly sensitive and stretchable sensor that enables the detection of pressure, strain, and human activity with facial expressions based on the highly aligned carbon nanotubes embedded in polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS). The aligned CNT network in PDMS modulates the electron conduction path in a unidirectional manner and provides multimodal mechanical sensing ability with a wide sensing range and high sensitivity. The highly aligned CNT sensor demonstrates high-pressure sensitivity (1.29 kPa−1), excellent stability and repeatability (over 10 000 cycles) with negligible hysteresis, and a good strain sensitivity over a wide range (up to 65%) with a good linear response. We confirmed the applicability of the sensor to detect small signals, such as heartbeat and pulse rate, expressions, and voice recognition, and that it could distinguish between various human motions with a very short recovery time of approximately 50 ms.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...