Anomalous restoration of sp2 hybridization in graphene functionalization†
Abstract
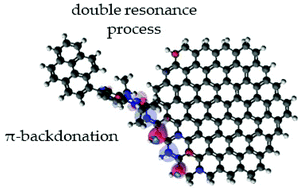
The functionalization of nanocarbon materials such as graphene has attracted considerable attention over the past decades. In this work, we designed and synthesized a unique N-heterocyclic carbene compound with a pyrene tail group (NHCp) to investigate how carbene species can be used for the functionalization of graphene. Although the carbene moiety of NHCp has the ability to covalently bond to graphene, the pyrene tail can noncovalently interact with graphene and allows monitoring its surrounding microenvironment. The major characteristics of the resulting nanohybrids were highly dependent on the type of graphene and the NHCp-to-graphene weight ratio. Importantly, despite the covalent functionalization of graphene, an anomalous decrease in the intensity of the Raman D peak and improved conductivity were observed for the nanohybrids. It was found that the covalent bond of NHCp to the graphene edge may allow the hybridization of their orbitals, which affects electronic energy levels and alters the double resonance process that originates the D peak at the edge defect. Importantly, the NHCp compound can act as a π acceptor (not just as a σ donor) via the NHCp–graphene covalent bridge. This is the first report showing that the concept of π-backdonation can be realized in two-dimensional materials, such as graphene, and rationally designed carbene molecules can functionalize graphene without losing their beneficial sp2 hybridization characteristics.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...