Electrochemical dual-aptamer biosensors based on nanostructured multielectrode arrays for the detection of neuronal biomarkers†
Abstract
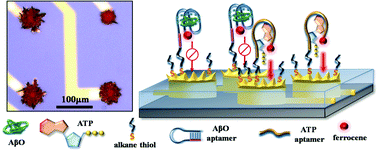
Multielectrode arrays (MEAs) have been increasingly used for the development of biosensors due to their capability to record signals from multiple channels, fast mass transfer rates, and high spatial resolution. Alzheimer's disease (AD) is often associated with mitochondrial dysfunction, which is closely related to reduced levels of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Therefore, simultaneous detection of ATP together with amyloid-β oligomers (AβO), a reliable biomarker for AD, can potentially advance the early detection of Alzheimer's disease. In this work, a dual-aptamer modified MEA chip was developed that consists of microelectrodes modified with electrodeposited 3D nanostructures (3D-GMEs). Electrodeposition methods, deposition potential, and deposition time were systematically altered and the active surface areas as well as the electrode morphologies were characterized by cyclic voltammetry and scanning electron microscopy. The nanostructured microelectrodes were sequentially modified with AβO and ATP specific aptamer receptors. To achieve the modification of different aptamer receptors at different 3D-GMEs of the same MEA chip, electrochemical cleaning was applied to individual 3D-GMEs. Ferrocene labels were attached to the aptamer receptors to enable amperometric signaling after target–aptamer binding. The developed aptasensor showed a linear detection range from 1 pM to 200 nM for the detection of AβO and from 0.01 nM to 1000 nM for the detection of ATP. Finally, ATP and AβO were detected simultaneously in the same analyte solution by the same sensor chip, which could support the early detection of AD, provide comprehensive information about the health status of the patient, and be helpful for pathological studies of neurodegenerative diseases.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...