Zn2+ stabilized Pd clusters with enhanced covalent metal–support interaction via the formation of Pd–Zn bonds to promote catalytic thermal stability†‡
Abstract
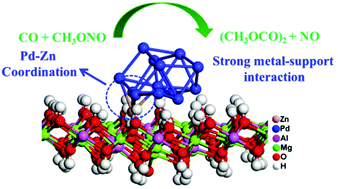
Pd-Based heterogeneous catalysts have been demonstrated to be efficient in numerous heterogeneous reactions. However, the effect of the support resulting in covalent metal–support interaction (CMSI) has not been researched sufficiently. In this work, a Lewis base is modulated over MgAl-LDH to investigate the support effects and it is further loaded with Pd clusters to research the metal–support interactions. MgAl-LDH with ultra-low Pd loading (0.0779%) shows CO conversion (55.0%) and dimethyl oxalate (DMO) selectivity (93.7%) for CO oxidative coupling to DMO, which was gradually deactivated after evaluation for 20 h. To promote the stability of Pd/MgAl-LDH, Zn2+ ions were introduced into the MgAl-LDH support to strengthen the CMSI by forming Pd–Zn bonds, which further increased the adsorption energy of the Pd clusters on ZnMgAl-LDH, and this was verified by X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) measurements and density functional theory (DFT) calculations. The stability of the Pd/ZnMgAl-LDH catalyst could be maintained for at least 100 h. This work highlights that covalent metal–support interactions can be strengthened by forming new metal–metal bonds, which could be extended to other systems for the stabilization of noble metals over supports.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Celebrating 60 years of the Fujian Institute of Research on the Structure of Matter


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...