Targeting and extending the eukaryotic druggable genome with natural products: cytoskeletal targets of natural products
Abstract
Covering: 2014–2019
We review recent progress on natural products that target cytoskeletal components, including microtubules, actin, intermediate filaments, and septins and highlight their demonstrated and potential utility in the treatment of human disease. The anticancer efficacy of microtubule targeted agents identified from plants, microbes, and marine organisms is well documented. We highlight new microtubule targeted agents currently in clinical evaluations for the treatment of drug resistant cancers and the accumulating evidence that the anticancer efficacy of these agents is not solely due to their antimitotic effects. Indeed, the effects of microtubule targeted agents on interphase microtubules are leading to their potential for more mechanistically guided use in cancers as well as neurological disease. The discussion of these agents as more targeted drugs also prompts a reevaluation of our thinking about natural products that target other components of the cytoskeleton. For instance, actin active natural products are largely considered chemical probes and non-selective toxins. However, studies utilizing these probes have uncovered aspects of actin biology that can be more specifically targeted to potentially treat cancer, neurological disorders, and infectious disease. Compounds that target intermediate filaments and septins are understudied, but their continued discovery and mechanistic evaluations have implications for numerous therapeutic indications.
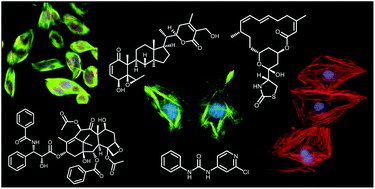
- This article is part of the themed collection: Targeting and extending the eukaryotic druggable genome with natural products


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...