Charge-assisted hydrogen bond and nitrile⋯nitrile interaction directed supramolecular associations in Cu(ii) and Mn(ii) coordination complexes: anticancer, hematotoxicity and theoretical studies†
Abstract
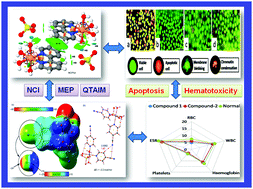
Two new coordination complexes of Cu(II) and Mn(II), viz., [Cu(bpy)(H2O)4]SO4·2H2O (1) and [Mn(4-CNpy)2(H2O)3SO4]·H2O (2) (bpy = 2,2′-bipyridine, 4-CNpy = 4-cyanopyridine), have been synthesized and characterized by using single crystal X-ray diffraction, elemental analysis, FT-IR spectroscopy, electronic spectroscopic techniques and TGA. The crystal structure of 1 uncovers the formation of sulfate–water assemblies involving lattice and coordinated water molecules, while complex 2 reveals the presence of unconventional weak T-shaped CN⋯CN contacts in the layered architecture. We have analysed the unconventional interesting interactions using DFT calculations, molecular electrostatic potential (MEP), the NCI plot and QTAIM computational tools. The interaction energies of the two H-bonded dimers in 1 are very large because of the coulombic attraction between the dicationic H-bonded donor and the dianionic acceptor. It is interesting to observe that despite the energy of the H-bonds being very small compared to the total dimerization energy, the final geometry of the assembly in 1 is due to the charge assisted directional H-bonds instead of the non-directional ion-pair interactions. The DFT study reveals that the T-shaped CN⋯CN interaction in 2 is very weak, in good agreement with the small MEP energy at the nitrile carbon atom. Anticancer studies of the compounds have been carried out using Dalton's lymphoma cell line using MTT and apoptosis assay. The results of compound 1 and 2 mediated cell cytotoxicity on the DL cancer cell line showed a significant concentration-dependent reduction in cell viability, while negligible cytotoxicity was observed in normal (PBMC) cells. The docking simulation results also confirm the interaction of the complexes with the active sites of amino acids of the target proteins. Furthermore, pharmacophore models (2D and 3D) for the compounds were mapped to the H-bond donor, positive ionisable area and hydrophobic features that are important for establishing biological activities. No hematotoxicity was recorded for the compounds after treatment in normal mice.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...