Biomimetic hydroxyapatite/silkfibre/methylcellulose composites for bone tissue engineering applications†
Abstract
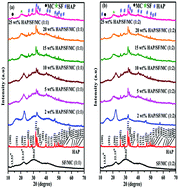
Hydroxyapatite (HAP)/silk fibre (SF)/methylcellulose (MC) composites were developed by an electrospinning (E-Spin) method. XRD, FTIR, TGA, DSC and SEM-EDAX results showed strong chemical interactions between the HAP, SF and MC. The mechanical properties of the composite were analyzed and the results showed that the tensile strength and elongation at break (%) of electrospun composites were in the range of 25.39–102.93 MPa and 39.48–288 MPa respectively. An increase in the tensile strength with an increase in the porosity (66.24–90.11%) was observed. In vitro antimicrobial activity was examined against Gram positive bacteria (S. aureus and B. subtilis), Gram negative bacteria (E. coli) and also against fungi (C. albicans). Moreover, in vitro bioactivity of the electrospun composite was studied by immersing the samples in simulated body fluid for 28 days. The ability to form new apatite on the surface of the electrospun composite was analyzed using XRD, FTIR and SEM-EDX. The ICP-OES (inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrometry) technique was used to examine the leaching of Ca and P ions from the SBF. An in vitro hemolytic study indicated that all samples were non-hemolytic (less than 1%). Human osteoblast cell proliferation results clearly indicated that the presence of HAP on the surface of the SF/MC composite promoted cellular adhesion, proliferation and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity when compared to the SF/MC composite without HAP.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...