A new multinebulizer for spectrochemical analysis: wear metal determination in used lubricating oils by on-line standard dilution analysis (SDA) using inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP OES)†
Abstract
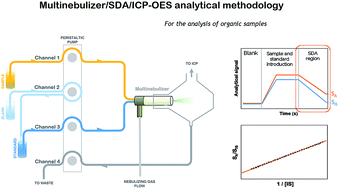
A new multinebulizer has been employed for wear metal (e.g., Cd, Cr, Cu, Fe, Mn, Ni, and Pb) determination in used lubricating oils. To this end, a multinebulizer-based analytical methodology combined with on-line standard dilution analysis (on-line SDA) and inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP OES) (multinebulizer/SDA/ICP OES) has been proposed, which is able to overcome typical limitations related to organic sample analysis by ICP-based techniques. This is accomplished by the simultaneous introduction of organic samples and aqueous calibration standards, with a minimal sample pretreatment (i.e., dilution). The multinebulizer/SDA/ICP OES combination allows the determination of Cd, Cr, Cu, Fe, Mn, Ni and Pb in used lubricating oils with a limit of detection of 20, 10, 6, 20, 4, 30 and 200 ng g−1, respectively. The subsequent analysis of spiked commercial lubricating oil samples has led to recovery values which range from 91 to 108%. The efficiency of the proposed methodology has been checked by comparing its results with values obtained with conventional standard addition calibration and both limits of detection and recovery values were of the same order of magnitude. The proposed analytical methodology has the main advantage of ease of operation, as time and cost of analysis are reduced and the use of organic calibration standards is also avoided. Hence, the synergistic association multinebulizer/SDA is a simple, fast, relatively economic, environmentally friendly, direct and reliable method of wear metal monitoring in used lubricating oils by ICP OES.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...