Eugenol and capsaicin exhibit anti-metastatic activity via modulating TGF-β signaling in gastric carcinoma†
Abstract
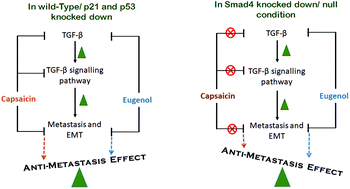
The transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) signaling is considered to be a key player in gastric cancer metastasis, and the inhibition of the TGF-β/SMAD4 signaling pathway may be a novel strategy for therapeutic interventions in cancer. Here, the anti-metastatic activity of two phytochemicals, eugenol and capsaicin, has been studied, and their potential to antagonize TGF-β has been investigated in gastric cancer cells. Both the phytochemicals exhibited anti-metastatic activity by inhibiting the TGF-β signaling pathway independent of P21 or P53, with capsaicin proving to be more potent than eugenol. However, unlike eugenol, the inhibitory effect of capsaicin on the TGF-β signaling pathway and metastasis was found to be dependent on SMAD4, which was validated in SMAD4-knocked down AGS cell and SMAD4-null SW620 cell line. Furthermore, the use of recombinant TGF-β and TGF-β receptor inhibitor LY2109761 confirmed that the anti-metastatic activity of eugenol is partially and that of capsaicin is principally mediated through the TGF-β signaling pathway. Identifying phytochemicals with the potential to inhibit cancer metastasis by targeting the TGF-β signaling pathway has immense scope for developing a therapeutic strategy against cancer metastasis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...