Asiatic acid ameliorates obesity-related osteoarthritis by inhibiting myeloid differentiation protein-2†
Abstract
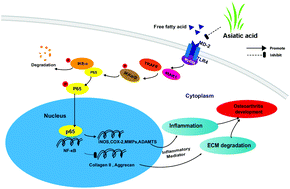
Obesity is related to osteoarthritis (OA). Aberrant lipid metabolism results in increased levels of free fatty acids, such as palmitate (PA), leading to inflammatory responses and excess catabolism of chondrocytes. Asiatic acid (AA), a plant anti-inflammatory compound, has been reported to exert protective effects for several diseases, but its effect on obesity-related OA is still unclear. The aim of this study is to evaluate the chondro-protective effect of AA on PA-induced human chondrocytes and a high fat diet (HFD)-fed mouse cartilage degeneration model. In vitro, the levels of the inflammatory and extracellular matrix (ECM) markers of chondrocytes after being treated with PA (500 μM) and AA (2.5–10 μM) were determined using western blotting and immunofluorescence enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). In vivo, after the oral administration of HFD and AA, X-ray examination, safranin O staining, and ELISA assay were conducted to evaluate cartilage calcification and degeneration and cytokine and adipokine levels in the serum of mice. AA treatment eliminated the inflammation caused by PA and extracellular matrix degradation. Mechanistically, AA blocked the stimulation of the NF-κB pathway. Analysis with co-immunoprecipitation and molecular docking indicated that the MD-2/TLR4 complex was a target of AA. In vivo, AA treatment not only prevented HFD-induced OA changes but also reduced proinflammatory cytokine and adipokine production in obese mice. AA exerted a chondroprotective effect by inhibiting the TLR4/MD-2 axis, thus showing promise for treating obesity-related OA.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...