Selenoproteins and renal programming in metabolic syndrome-exposed rat offspring
Abstract
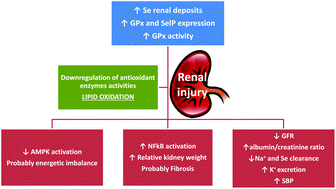
Maternal metabolic syndrome (MS) during gestation and lactation leads to several cardiometabolic changes related to selenium (Se) status and selenoprotein expression in offspring. However, little is known about kidney programming and antioxidant selenoprotein status in MS pups. To gain more knowledge on this subject, two experimental groups of dam rats were used: Control (Se: 0.1 ppm) and MS (fructose 65% and Se: 0.1 ppm). At the end of lactation, Se deposits in kidneys, selenoprotein expression (GPx1, GPx3, GPx4 and selenoprotein P), oxidative balance and AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and activated transcriptional factor NF-κB expression were measured. Kidney functional parameters, albuminuria, creatinine clearance, aldosteronemia, and water and electrolyte balance, were also evaluated. One week later systolic blood pressure was measured. Lipid peroxidation takes place in the kidneys of MS pups and Se, selenoproteins and NF-κB expression increased, while AMPK activation decreased. MS pups have albuminuria and low creatinine clearance which implies glomerular renal impairment with protein loss. They also present hypernatremia and hyperaldosteronemia, together with a high renal Na+ reabsorption, leading to a hypertensive status, which was detected in these animals one week later. Since these alterations seem to be related, at least in part, to oxidative stress, the increase in Se and selenoproteins found in the kidneys of these pups seems to be beneficial, avoiding a higher lipid oxidation. However, in order to analyze the possible global beneficial role of Se in kidneys during MS exposure, more data are necessary to document the relationships between GPx4 and NF-κB, and SelP and AMPK in kidneys.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Food & Function Recent HOT articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...