Bifidobacterium adolescentis and Lactobacillus rhamnosus alleviate non-alcoholic fatty liver disease induced by a high-fat, high-cholesterol diet through modulation of different gut microbiota-dependent pathways†
Abstract
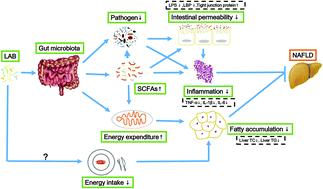
The incidence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) has increased year on year, and the increasing appreciation of the importance of gut microbiota provides novel therapeutic avenues for the treatment of NAFLD. To explore the similarities and differences between lactic acid bacteria (LAB) known to alleviate NAFLD, we selected three strains of Bifidobacterium adolescentis and three strains of Lactobacillus rhamnosus to administer to C57BL/6J mice on a high-fat, high-cholesterol diet (HFHCD) for 23 weeks. Subsequently, the effects of the LAB were evaluated through various measures. The six LAB strains were found to have varying degrees of efficacy in the prevention of NAFLD. We found that there were interspecific and intraspecific differences in the beneficial effects, mainly with respect to energy metabolism, lipid metabolism and short-chain fatty acid concentration. Three strains of B. adolescentis and one strain of L. rhamnosus were found to relieve NAFLD by increasing the concentration of short-chain fatty acids in the intestine of NAFLD mice. The other two strains of L. rhamnosus, LGG and L10-1, relieved NAFLD through different ways, LGG modulated energy metabolism and lipid metabolism, and L10-1 reduced liver inflammation. Examination of gut microbiota indicated that the six LAB strains could block the HFHCD-induced elevation of Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes and alter the dominant species within the gut. These results suggest that B. adolescentis and L. rhamnosus can inhibit the development of NAFLD by regulating gut microbiota, and their use is thus a promising therapeutic strategy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...