Lactic acid bacteria reduce diabetes symptoms in mice by alleviating gut microbiota dysbiosis and inflammation in different manners†
Abstract
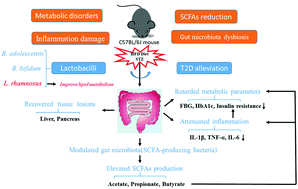
The prevalence of diabetes mellitus is increasing worldwide. Lactic acid bacteria have shown efficacy in alleviating diabetes. We studied the remission effect of nine strains of lactic acid bacteria on the symptoms of high-fat diet- and streptozotocin-induced type 2 diabetes and its mechanism in mice. The oral administration of Bifidobacterium adolescentis, B. bifidum or Lactobacillus rhamnosus to mice every day for more than 12 weeks showed that the individual strains could reduce the fasting and postprandial blood sugar levels, improve glucose tolerance and prevent pancreatic damage. However, L. rhamnosus strains showed greater efficacy than Bifidobacterium strains in the regulation of blood lipid levels. The effects of lactic acid bacteria on the recovery of glycolipid metabolism disorder and gut microbiota dysbiosis showed inter- and intraspecific differences. In addition, the strains that exhibited hypoglycaemic effects played a beneficial role in reducing insulin resistance by contributing to the production of short-chain fatty acids and alleviation of inflammation. The ability of lactic acid bacteria to reduce inflammation was found to be closely related to their ability to alleviate diabetes mellitus.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Food & Function Recent HOT articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...