Tangeretin mitigates l-NAME-induced ventricular dysfunction and remodeling through the AT1R/pERK1/2/pJNK signaling pathway in rats
Abstract
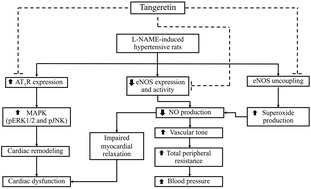
Tangeretin is a citrus flavonoid that exerts several beneficial effects, including anti-inflammation, anti-oxidation and neuroprotection. In this study, the aim was to test the effect of tangeretin on Nω-Nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME)-induced high blood pressure, and left ventricular dysfunction and remodeling in rats. Rats were divided into five groups (n = 8 per each group): a control group, an L-NAME group and three L-NAME groups treated with tangeretin (15 mg kg−1) or tangeretin (30 mg kg−1) or captopril (5 mg kg−1) for the final two weeks. After five weeks of experiment, L-NAME groups had high systolic blood pressures, and ventricular dysfunction and remodeling. Overexpression of angiotensin II type 1 receptor, phosphorylated-extracellular-regulated kinase 1/2 (pERK1/2), and phosphorylated-c-Jun N-terminal kinase (pJNK) protein but downregulation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) protein expression in ventricular tissues were observed in hypertensive rats while the protein expression of phosphorylated-mitogen activated protein kinase p38 did not differ among groups. The decrease in plasma NOx and increase in vascular superoxide generation, plasma malondialdehyde, angiotensin-converting enzyme activity and angiotensin II levels were found in hypertensive rats. These alterations were suppressed in hypertensive rats treated with tangeretin or captopril. In conclusion, tangeretin exhibits antihypertensive effects and alleviates ventricular dysfunction and remodeling in hypertensive rats. These effects are associated with the inhibition of renin angiotensin system activation and restoration of pERK1/2, pJNK, and eNOS protein expressions along with reduced oxidative stress and increased NO bioavailability.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Food & Function Recent HOT articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...